In today’s world, financial stability is crucial, thus understanding the accounting principles of economics can be vital in maintaining that stability. Economic principles are the cornerstone of modern economics and give a framework for understanding how economic agents behave and interact in diverse economic circumstances. By applying these principles to our personal finances, we can make informed decisions and avoid financial pitfalls that can lead to bankruptcy. This article will explore some essential economic principles and discuss how they can help you manage your finances effectively and ultimately avoid bankruptcy’s devastating consequences. Let us delve into how the principles of economics can facilitate financial stability and success.
Table of Contents
- 1. Economic Entity Principle: What is it?
- 2. Example of Economic Entity Principle
- 3. Significance of the Business Entity Concept
- 4. Challenges of the economic entity principle
- 5. Conclusion
- 6. FAQs
Economic Entity Principle: What is it?
The economic entity principle, a financial accounting concept, states that a business organization should be treated as a separate and distinct entity from its owners, investors, and other businesses. This principle requires that all business financial transactions be recorded and reported separately from the company’s owner’s or other entity’s personal financial transactions. The Infographic image showed several types that can be recognized under this principle.
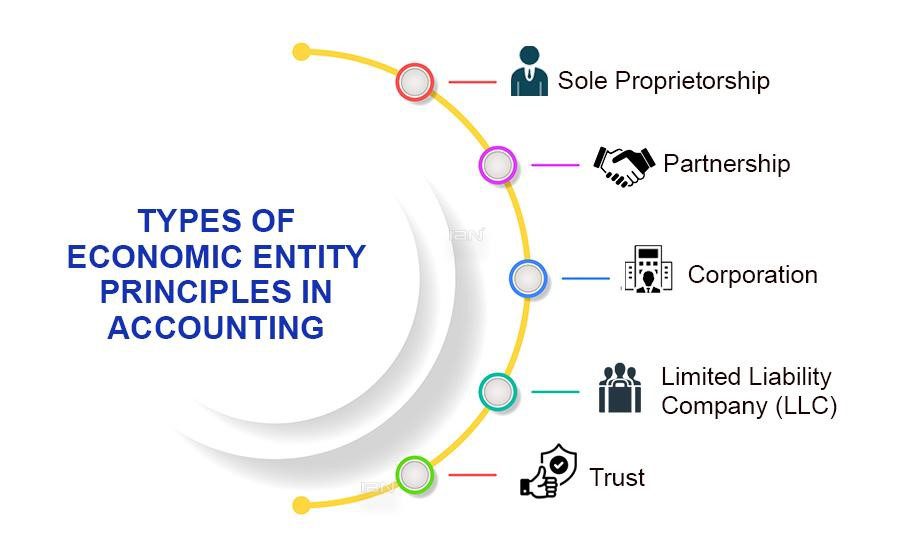
In practical terms, businesses must maintain their financial records and statements, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements, which should solely capture the business’s financial transactions, including revenue earned, expenses incurred, assets owned, and liabilities owed.
By adhering to the economic entity principle, businesses can ensure that their financial information is accurate and dependable, facilitating informed decision-making. This information can be utilized by investors, creditors, and other stakeholders to evaluate the financial performance and viability of the business and inform their investment or lending decisions accordingly.
Example of Economic Entity Principle
The economic entity principle is a fundamental tenet of accounting that necessitates segregating a company’s financial activities from those of its owners or related entities. This principle is illustrated clearly when a business owner seeks to expand their operations, such as in the hypothetical scenario of John, the proprietor of a coffee shop who intends to establish a new bookstore.
To comply with the economic entity principle, John must create a distinct legal entity, such as a corporation or an LLC, for the new bookstore. This new business would operate independently of the coffee shop, maintaining its financial records and accounts.
As a result, the bookstore would have its bank account, generate revenue, and incur expenses, all of which would be documented separately from the coffee shop. To ensure that each business’s financial performance is accurately reflected in its financial statements, the financial transactions of the coffee shop and the bookstore must be recorded separately.
By adhering to the economic entity principle, John can effectively monitor the accounting health of each business and make informed decisions based on their unique financial statements. Furthermore, this principle serves to prevent any discrepancies arising from transactions between related entities, thereby ensuring the accuracy and integrity of the financial accounts.
Significance of the Business Entity Concept
Ensuring compliance with applicable laws and regulations concerning financial and legal liabilities.
Generating precise financial statements for taxation and business planning.
Determining applicable tax rates for separate entities.
Analyzing business performance for strategic decision-making.
Engaging external auditors for attestation services.
Comparing financial metrics with competitors.
Maintaining separate records for multiple businesses.
Meeting reporting requirements of shareholders and lenders.
Challenges of the economic entity principle
This principle must be followed to keep accurate and transparent financial records, but applying it might provide some difficulties for accountants. Some of the key challenges of the economic entity principle in accounting include the following:
Identifying the boundaries of the economic entity, which can be difficult in complex business structures.
Accounting for intercompany transactions, which can be complex and require careful documentation.
Accounting for the impact of legal structures on financial reporting
Measuring the performance of a specific entity can be difficult when dealing with a complex business structure.
Creating reliable financial statements that are not misleading.
While adhering to the economic entity principle is essential for ensuring accurate financial reporting, it can be challenging to record transactions, account for intercompany transactions, measures performance, and create reliable financial statements. Therefore, accountants must exercise care and diligence when applying this principle to financial reporting.
Conclusion
The economic entity principle presumes that businesses are distinct from their proprietors and other entities. Nonetheless, the practical application of this principle may pose challenges, particularly in cases involving multiple entities. IBN Tech professionals precisely manage spending, revenue, and other financial indicators necessary for making educated business decisions by keeping complete records for each corporate unit. Our experts can identify potential financial hazards and help the business make better financial decisions, improve its account management practices, and avoid potential financial issues that could lead to bankruptcy.
economic entity principle FAQ’s
- Q.1 What is the importance of the economic entity principle?
- The economic entity principle is important because it assists businesses in keeping accurate financial records and avoiding financial problems. Businesses can make informed decisions, avoid legal liability, and encourage investment by segregating the financial transactions of various businesses.
- Q.2 How does the economic entity principle help prevent bankruptcy?
- The economic entity principle helps in the prevention of bankruptcy by assuring accurate financial reporting/ forecasting and improved accounting management. Businesses can recognize possible financial risks early and take proactive measures to mitigate them by separating the financial transactions of various organizations. These can involve actions to cut costs, increase revenue, or obtain finance.
- Q.3 What are some examples of the economic entity principle in practice?
- The economic entity principle examples are implemented by using separate bank accounts for business and personal funds, tracking business spending separately from personal expenses, and recording business transactions separately from personal transactions.

